Picture this: An AI rejects your loan application, but the bank cannot explain why. Welcome to the AI black box problem, which has implications for healthcare, finance, and other industries. As artificial intelligence impacts our society, its opaque decision-making presents critical issues of trust, ethics, and safety. This article delves into the AI black box problem, explaining what it is, why it matters, and its impact on industries and daily life. Whether you’re new to AI or a tech veteran, you’ll find clear ideas, real-world examples, and answers to your most pressing issues concerning AI transparency.
What is the AI Black Box Problem?
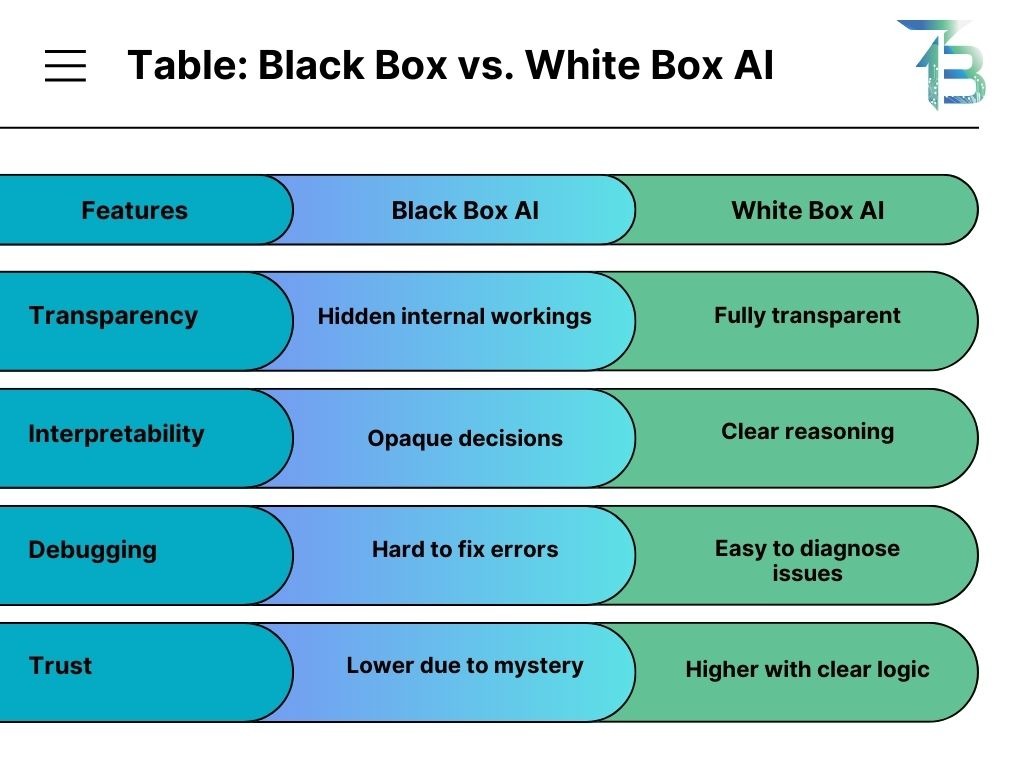
The AI black box problem refers to the lack of transparency in how complex artificial intelligence (AI) systems, particularly deep learning models, make choices. Consider AI to be similar to human intuition: we recognize a friend’s face without explaining why, but this ambiguity in AI can have major effects.
Key Characteristics:
- The inputs and outputs are apparent, but the fundamental logic is hidden.
- Most prevalent in deep learning with millions of parameters.
- Even professionals in AI find it challenging to interpret.
Example: An AI rejects a job candidate, but no one can explain why, leaving an opportunity for bias or inaccuracy.
Why is the AI Black Box Problem Important?
Opaque AI systems raise ethical, legal, safety, and trust concerns that require attention.
1. Ethical and Legal Risks:
Bias and Discrimination: Unexplained loan denials may indicate bias.
Regulatory Compliance: Laws such as the EU AI Act and the GDPR’s “right to explanation” mandate transparency.
2. Safety Concerns:
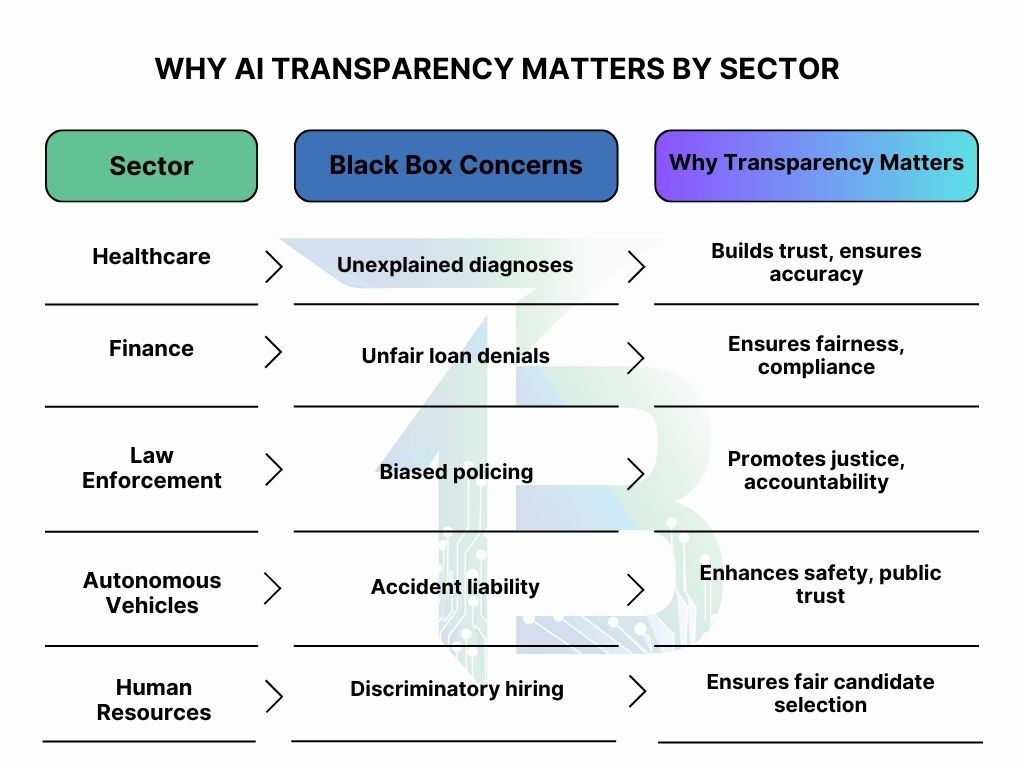
Healthcare: Irrational diagnoses endanger lives.
Autonomous Vehicles: Uncertain decisions may result in accidents.
3. Trust:
Users and organizations are hesitant to accept AI that they don’t understand.
4. Security:
Opaque models are subject to data poisoning, which occurs when hackers modify training data without detection.
Solving the black box problem is critical to responsible AI deployment.
How Does AI’s Black Box Problem Work?
The AI’s black box problem derives from the intricacy of deep learning algorithms, which replicate human brain operations while concealing their reasoning processes.
Process:
Input: Data (such as images or text) enters the system.
Processing: Neural networks with hidden layers find patterns using vector embeddings, which are numerical data representations. Non-linear reasoning complicates the traceability of decision routes.
Output: A decision is made, but the “why” is buried in millions of calculations.
Why It’s Obscure:
Unlike rule-based systems, deep learning alters reasoning dynamically, making it less understandable.
Explainable AI (XAI) approaches, such as LIME and SHAP, seek to make these processes explicit by displaying crucial decision criteria.
What Are the Benefits of Solving AI’s Black Box Problem?
Transparency in AI leads to considerable benefits across businesses:
- Healthcare: Explained diagnoses foster trust as well as precision.
- Finance: Clear loan or fraud detection methods avoid unfair rejections.
- Law enforcement: Transparent predictive policing lowers bias and promotes justice.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Making informed driving decisions improves safety and accountability.
- Human Resources: Transparent hiring algorithms reduce discrimination.
Read more: How AI Mimics Human Thought: Neural Networks Explained
What are the Common Myths About AI Black Box Problems?
Misunderstandings of the AI black box problem can cause confusion. Let’s clear the air by addressing some prevalent myths.
Myth: All artificial Intelligence is a Black Box.
Truth: Not all AI systems are opaque. Simpler models, such as decision trees or linear regression, have clear, understandable reasoning. The black box issue typically impacts big deep learning models with millions of parameters, making tracing decisions difficult. In contrast to a neural network used to forecast credit scores, a rule-based AI for tax calculations can be completely transparent.
Myth: Explainable AI Reduces Performance.
Truth: Explainable AI (XAI) does not always imply lower accuracy. Techniques such as LIME and SHAP provide insights into complex models while preserving their power. In some circumstances, simpler, interpretable models can outperform black box systems, particularly for structured data, as demonstrated by studies such as the Explainable Machine Learning Challenge.
Myth: Black Box Models are Inherently More Accurate.
Truth: The premise that complexity equates to higher performance is erroneous. For certain objectives, such as fraud detection with clear patterns, interpretable models like logistic regression can compete with or outperform deep learning algorithms. The Explainable Machine Learning Challenge established that transparency and accuracy can coexist, dispelling the “black box or bust” myth.
Myth: Explainability Slowed AI down.
Truth: XAI approaches aim to strike a balance between speed, accuracy, and transparency. While increasing interpretability may involve additional work in some circumstances, contemporary techniques such as SHAP are designed to deliver explanations rapidly. Furthermore, openness can accelerate adoption by increasing confidence, outweighing tiny processing trade-offs.
Myth: The black box issue is unsolvable.
Truth: Advances in explainable AI are reducing the mystery. Methods such as model visualization, feature importance analysis, and hybrid models are making AI more understandable. While perfect transparency for the most sophisticated systems may be difficult, continuous research is bridging the gap, ensuring that AI is both powerful and understandable.
Conclusion
As AI reshapes healthcare, finance, law enforcement, and other industries, the black box problem becomes increasingly important. Transparency is vital for maintaining trust, ethics, and safety. Explainable AI (XAI) is advancing, and legislation such as the EU AI Act strives for responsibility; thus, the future of comprehensible AI looks promising. However, the road begins with consciousness. Would you put your trust in an inexplicable AI? Please share your ideas below!
